Rate of Reaction
Rate of Reaction: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Rate of a Chemical Reaction,Average Rate of a Reaction,Instantaneous Rate of a Reaction etc.
Important Questions on Rate of Reaction
In a pseudo first order hydrolysis of ester in water, the following results are obtained:
| in seconds | ||||
(i) The average rate of reaction between the time interval 30 to 60 seconds and
(ii) The pseudo first order rate constant for the hydrolysis of ester is?
The ratio of disappearance of B is The rate of reaction and rate of change in concentration of A and C would be:
The unit of rate of reaction is _____.
The quantitative estimation of change in the rate of reaction with change in concentration does not always follow stoichiometric equation. Justify.
The slope obtained by drawing a tangent at time on the curve for the concentration of reactants vs time is equal to instantaneous rate.
If the rate with respect to and are, respectively then the corresponding chemical equation is .
What are the units for the rate of the reaction ?
For a reaction is in , what is the average rate of reaction?
If for the formation of from and is , then for decomposition of mole of is _____.
Enter your correct answe as A, B or C.
In the reaction , if initial concentration of hydrogen is kept constant and the concentration of is doubled, the rate of reaction increases by four times. This shows that rate is directly proportional to _____.
The rate of _____ reactions cannot be determined experimentally.
In the reaction , if is increased by three times then the difference in the rate is _____ of the initial rate.
The above reaction was studied at by monitoring the concentration of in which initial concentration was and after half an hour became . The rate of production of is _______
(Nearest integer)
The number of given statement/s which is/are correct is_____
(A) The stronger the temperature dependence of the rate constant, the higher is the activation energy.
(B) If a reaction has zero activation energy, its rate is independent of temperature.
(C) The stronger the temperature dependence of the rate constant, the smaller is the activation energy.
(D) If there is no correlation between the temperature and the rate constant then it means that the reaction has negative activation energy.
If the following reaction , rate constant is. If we start with then Conc. of after ten minutes is
At high temperatures, ethyl chloride produces and ethylene by the following first order reaction:
In an experiment, when the initial concentration of ethyl chloride was , the rate of the reaction was found to be m/s. What will be the rate of reaction if the initial concentration of ethyl chloride is ?
Kamlesh was conducting an experiment to figure out the rate equation of the following reaction:
He measured the rate of this reaction as a function of initial concentrations of the reactants as follows:
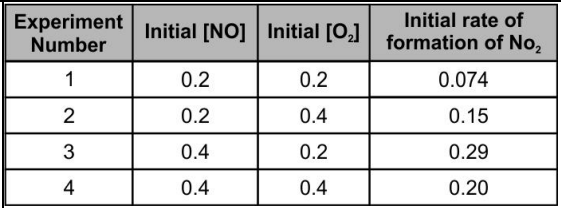
Which of the following could be a reason for the inconsistency in the initial rate of formation of data for experiment ?
In the reaction : , the rate of disappearance of B is . Find the rate of appearance of C.
In the reaction : , the rate of disappearance of B is . Find the rate of reaction.
